
- #Ventricular paced rhythm with failure to capture how to#
- #Ventricular paced rhythm with failure to capture generator#
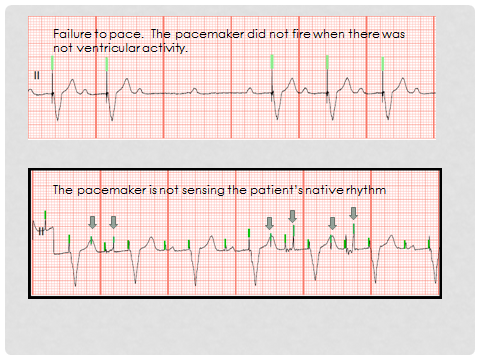
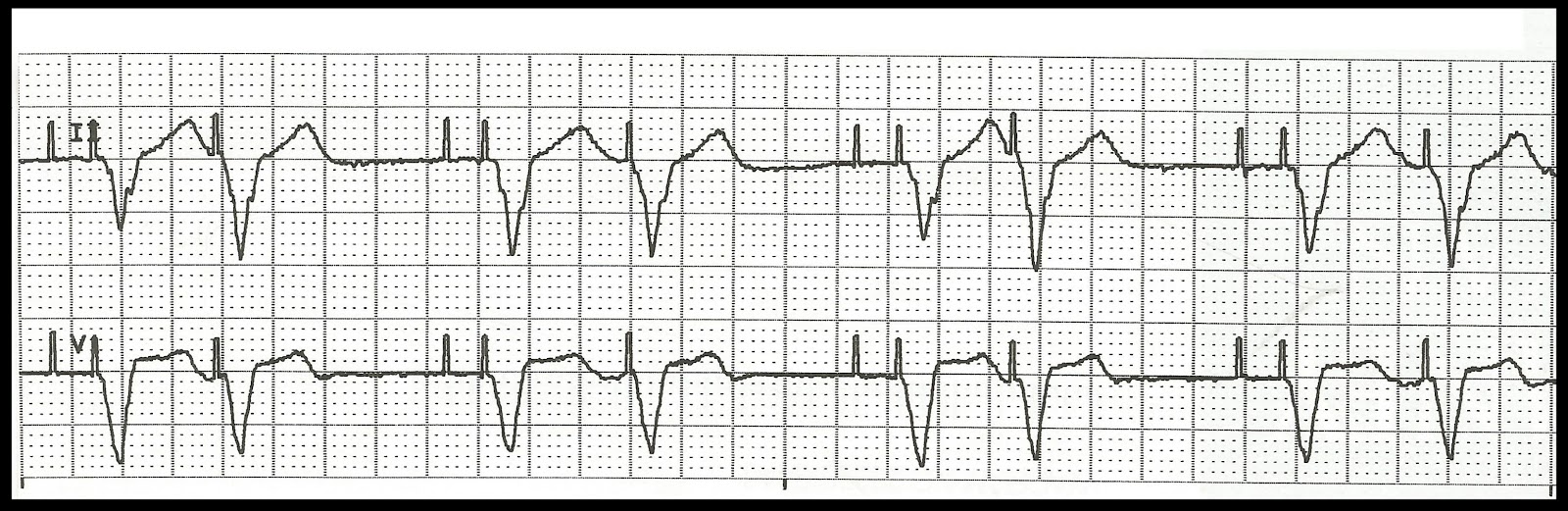
The pacer will trigger a ventricular beat if it senses an atrial beat (either paced or native) and there is no intrinsic ventricular beat within a programmed amount of time.Ventricular pacing is inhibited if a native ventricular beat is sensed.Atrial pacing is inhibited if a native atrial beat is sensed.The pacemaker will either trigger or inhibit pacing based on whether it senses native cardiac activity.Pacing is inhibited if pacer senses intrinsic ventricular activity.ĭDD: Both the atria and ventricle are paced and sensed.Ventricle will be paced regardless of native cardiac activity.VOO: The ventricle is paced asynchronously. The following are examples of typical codes: There is a 5-position code, of which the first 3 letters are the most relevant to the EM physician. Pacer codes describe the function of the pacemaker. AICD will have a thick coil that differentiates it from a pacemaker (as seen in AICD PA and Lateral Views).A common fracture site is between the first rib and the clavicle.

#Ventricular paced rhythm with failure to capture generator#
Compare pulse generator location with a prior CXR if available.Manufacturer code, which is found on pulse generator.A chest x-ray should be obtained to evaluate for: Pocket hematoma (bleeding associated with facial plane dissection for pocket creation)Īll cardiac pacemakers consist of a pulse generator and at least 1 lead connecting the generator to the myocardium.Venous thrombosis of the upper extremity.CHF with electromechanical ventricular dyssynchronyĪlthough relatively rare, complications from pacemaker implantation typically occur within the first 6 weeks of placement and include:.For sustained pause dependent VT, with or without QT prolongation.Recurrent syncope caused by spontaneously occurring carotid sinus stimulation and carotid sinus pressure that induces ventricular asystole of > 3 seconds.Symptomatic chronotropic incompetence (failure to achieve 85% of age-predicted maximal heart rate during formal or informal stress test or inability to mount age appropriate heart rate during activities of daily living).Some of the Class I indications for pacemaker insertion per the 2012 ACCF/AHA/HRS guidelines 3 include:
#Ventricular paced rhythm with failure to capture how to#
Can you distinguish between an abnormal EKG and a cardiac device malfunction at a glance, recall common pacer codes, or identify pacemaker problems on an X-ray?Īs the use of cardiac devices increases, 1-2 emergency physicians must know how to manage not only patients who may need a pacemaker, but also those who present to the ED with a device already implanted. This article summarizes the indications for pacemaker insertion, evaluating a pacemaker on a chest X-ray, understanding pacer codes, interpreting normal and abnormal EKG findings with paced rhythms, and pacer malfunctions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
